When there’s too much cholesterol in your bloodstream, it can build up inside the arteries that feed your heart, brain, and other organs. Over time, it can clog them and prevent enough blood from flowing to the heart, causing a heart attack or stroke.
Cholesterol is a waxy type of fat found all through your body, including your blood. It’s made by your liver, but the foods you eat also contain cholesterol. While we all need a certain amount of cholesterol for our bodies to function normally, having too much cholesterol in your bloodstream can cause health problems.
There aren’t any symptoms that let you know whether you have high cholesterol. Only a cholesterol test known as a lipid panel can measure the amount of cholesterol in your bloodstream.
Many patients get high cholesterol from a high cholesterol diet of saturated fats and animal products, like meat and dairy. For others, high cholesterol is genetic and runs in the family.
Other conditions can also lead to high cholesterol, such as:
If you have high cholesterol, several factors can lead to a greater risk of heart disease, including:
We offer comprehensive testing and treatment options in one location at the AHN Lipid Clinic. We have an experienced team, including cardiovascular experts who are board-certified lipidologists, pharmacists, dietitians, and exercise physiologists dedicated to helping you manage your cholesterol. We also offer several international clinical trials that are testing some of the latest therapies for high cholesterol.
You’ll have a blood test known as a lipid panel to measure the amount of cholesterol in your bloodstream, including:
A patient with a total cholesterol count of 200 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) is considered to have high cholesterol. High cholesterol is also measured by having an LDL cholesterol count of 160 mg/dL or higher and/or a triglyceride level > 200 mg/dL, especially if the HDL levels are low. Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is extremely high cholesterol levels with LDL, typically > 190 mg/dL. It is very common, occurring in 1 in 250 individuals.
Our team of cardiovascular experts, dietitians, and exercise physiologists help manage your cholesterol levels and significantly reduce the long-term risk of heart disease and stroke with medications and support for healthier lifestyles.
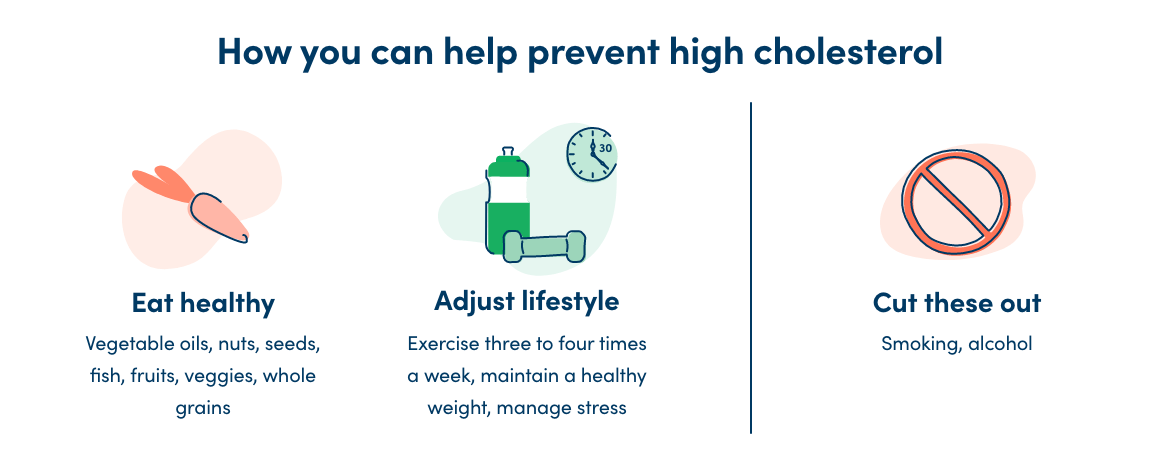
There are high cholesterol medications you can take to help lower cholesterol levels. We work closely with patients to create individual treatment plans, while acknowledging side effect of medications and drug interactions. However, making a few lifestyle changes can also help improve your cholesterol. These changes include:
Reducing foods high in saturated fats, like red meat and dairy products, can help lower your LDL cholesterol. Foods to eat if you have high cholesterol include items rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, flaxseed, and nuts. You’ll also want to increase your fruits and vegetable intake as well as soluble fiber intake with foods like oatmeal, Brussels sprouts, beans, pears, and apples.
Incorporating at least 30 minutes of exercise every day can help raise your HDL (good) cholesterol levels and lower your triglyceride levels. Losing weight can also help. However, the benefits of exercise are present even if you do not lose weight.
Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco products can help improve your HDL cholesterol levels.
Cutting down on the amount of alcohol you consume can help lower your cholesterol levels and help prevent heart disease overall.
Call (412) DOCTORS (412) 362-8677 or request an appointment to have your cholesterol checked or for help managing your high cholesterol.